Пилотные проекты: Таджикистан
Ледник Саидой Насафи (Баралмос) расположен в отдаленной горной долине и является домом для нескольких нестабильных озер, представляющих угрозу для жизненно важных дорог и населенных пунктов, расположенных ниже по течению. GLOFCA поддерживает целенаправленные усилия по снижению рисков и раннему предупреждению, чтобы защитить людей, инфраструктуру и экосистемы в этом опасном районе.
Пилотная площадка
-
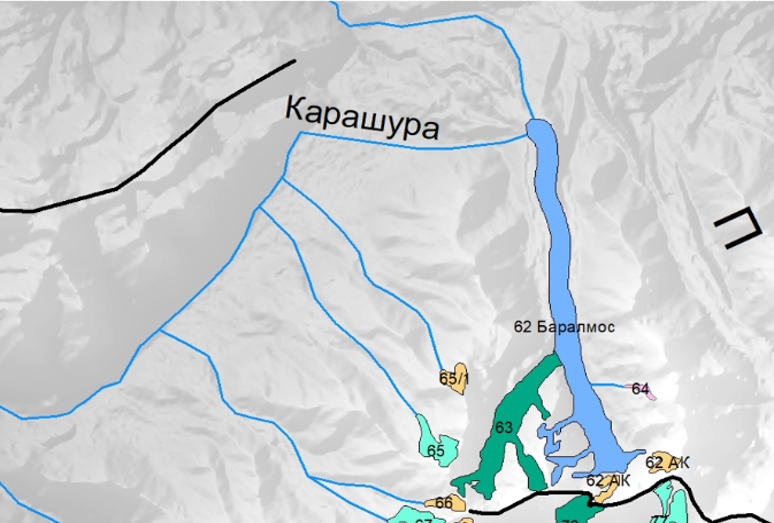
Обзор: Ледник Сайдой Насафи (Баральмос)
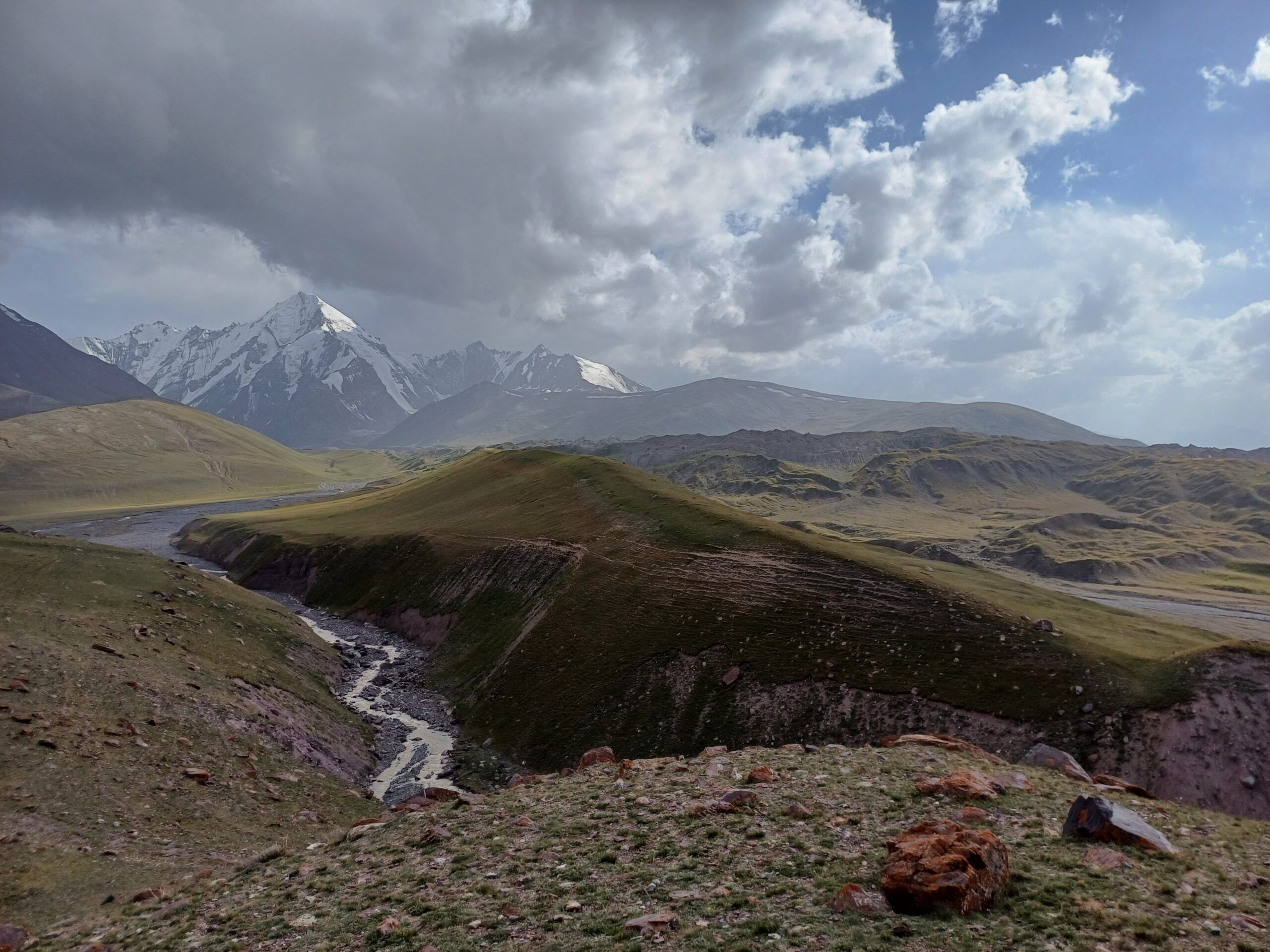
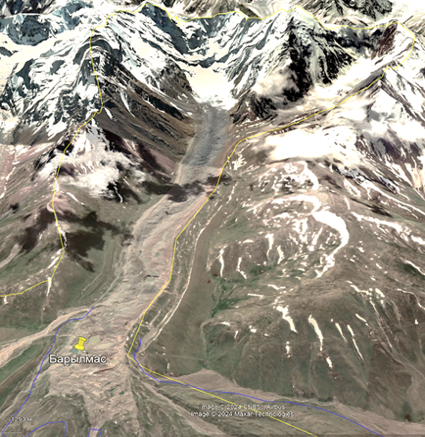
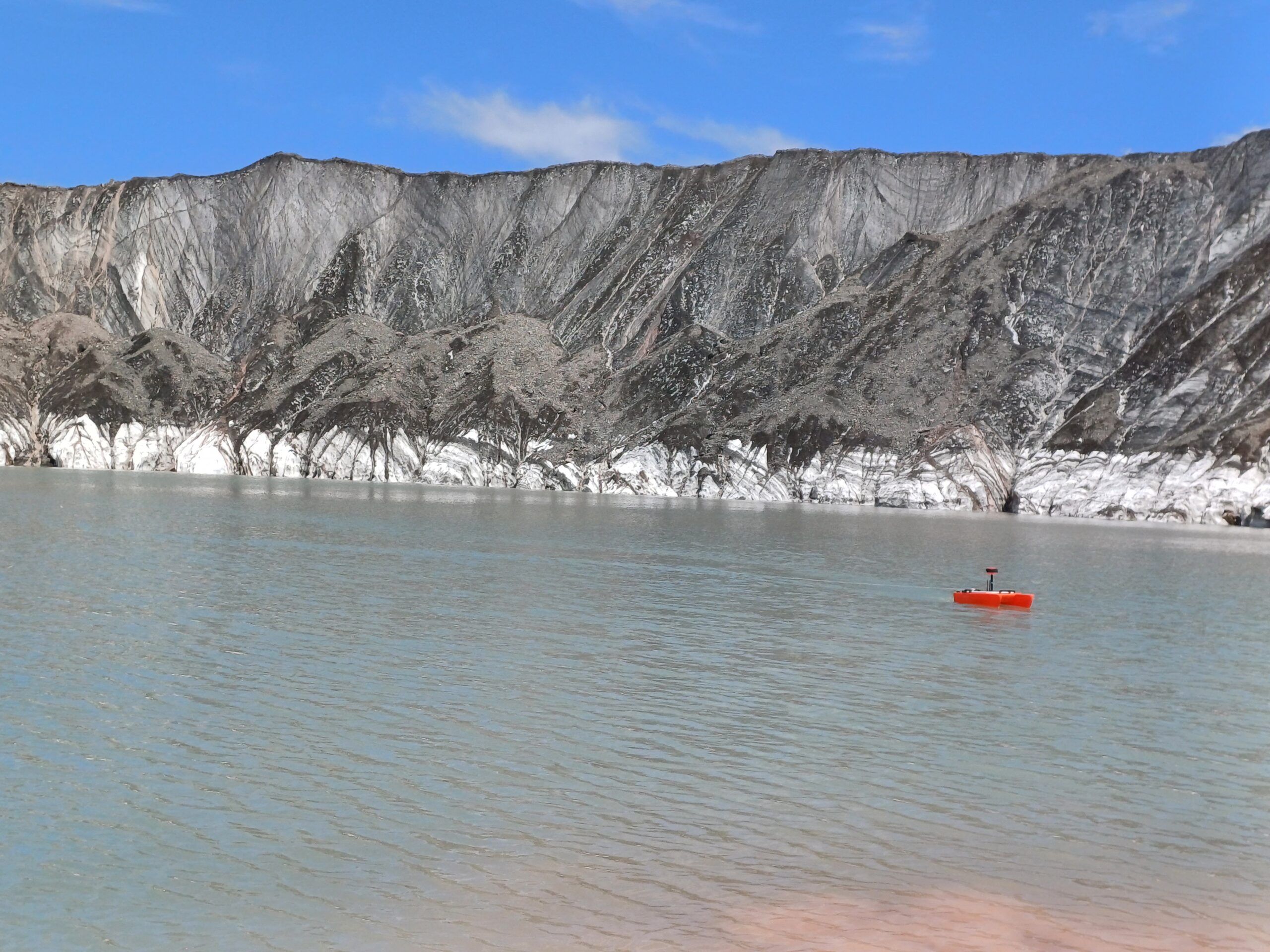
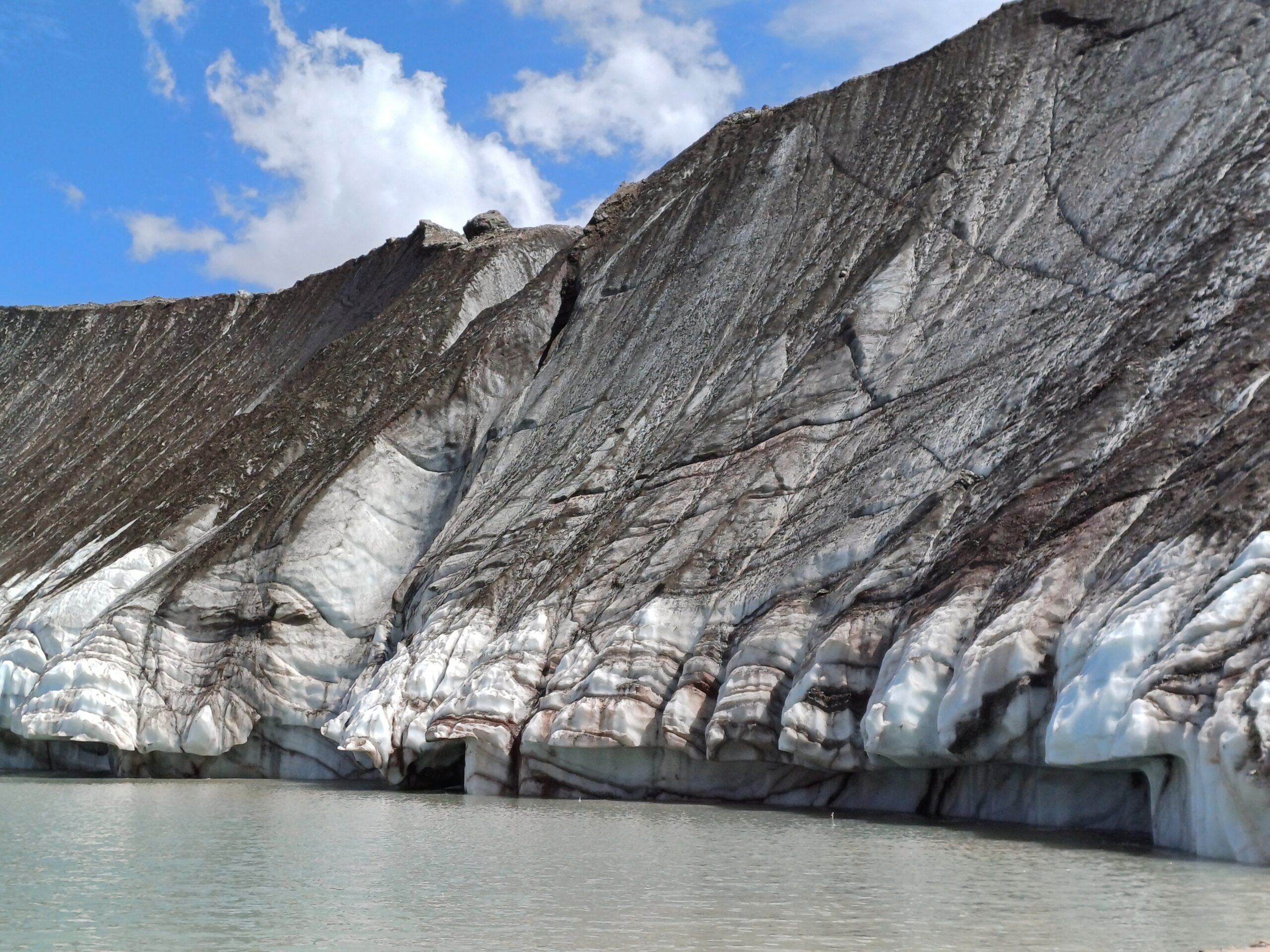
Ледник Сайдой-Насафи (Баралмос) - сложный долинный ледник, расположенный на северном склоне хребта Петра Первого (координаты: 39°03'17.05″ с.ш., 71°22'7.81″ в.д.). Он состоит из двух почти равных ледовых потоков и относится к типичным ледникам туркестанского типа. Его общая длина составляет 10,7 км, а площадь поверхности - 6,3 км².
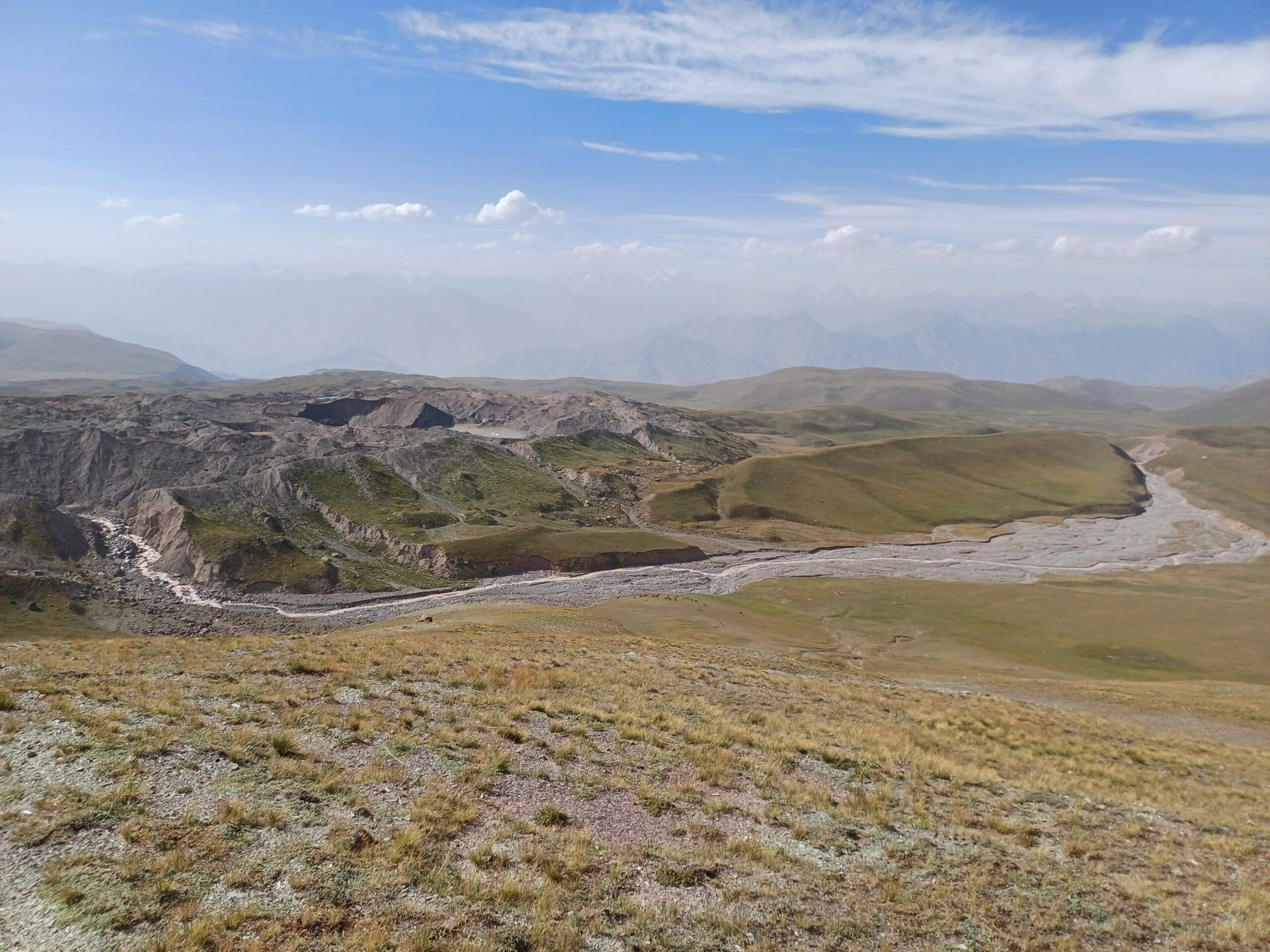
Языки ледника покрыты моренным материалом, а их поверхность отмечена эрозионными каналами и ледниковыми озерами. Талые воды ледника питают верховья реки Рагноу (приток Карашура) и частично попадают в бассейн реки Сурхоб.
Зона аккумуляции включает лавиноопасные конусы в основании окружающих склонов. Фирновая линия соответствует нижнему краю этих конусов, что свидетельствует о сложных условиях аккумуляции.
В регионе выпадает большое количество осадков на южных и юго-западных склонах - до 2 000 мм в год и более. Большая часть осадков выпадает зимой и весной, в то время как летние месяцы (июль-сентябрь), совпадающие с абляцией ледников, являются самыми сухими. Речной сток в бассейне формируется в основном за счет таяния ледников, сезонного снега и грунтовых вод, на долю последних приходится около 30% годового стока.
-
Воздействие опасностей и риск
Таджикистан сталкивается с высоким уровнем природных угроз: около 85% территории страны подвержено селям, а 32% считается зоной высокого риска. Районы республиканского подчинения (РРП), где расположен данный пилотный участок, являются одними из самых уязвимых, здесь зарегистрировано наибольшее количество опасных процессов, включая сели, оползни, наводнения и эрозию.
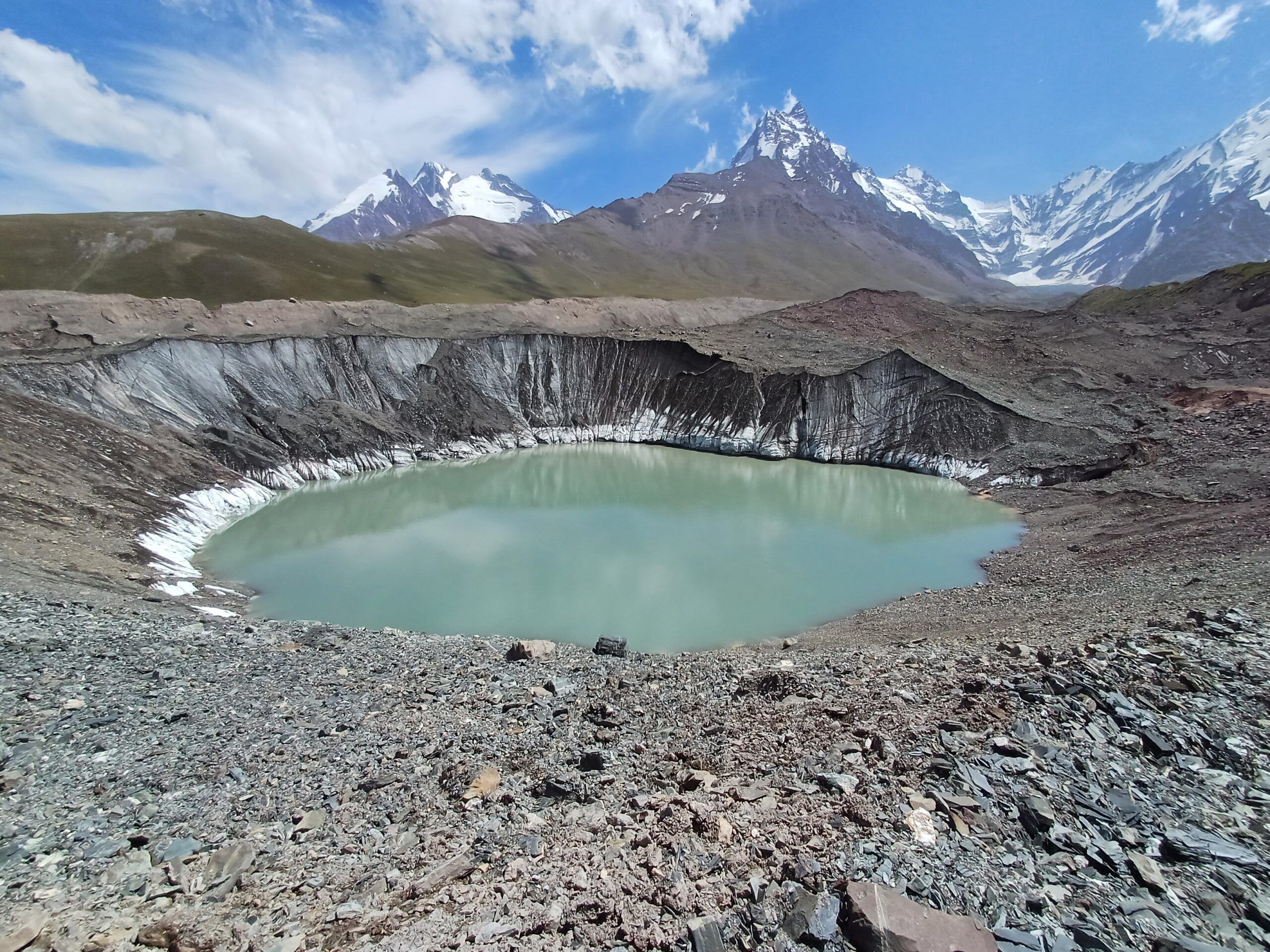
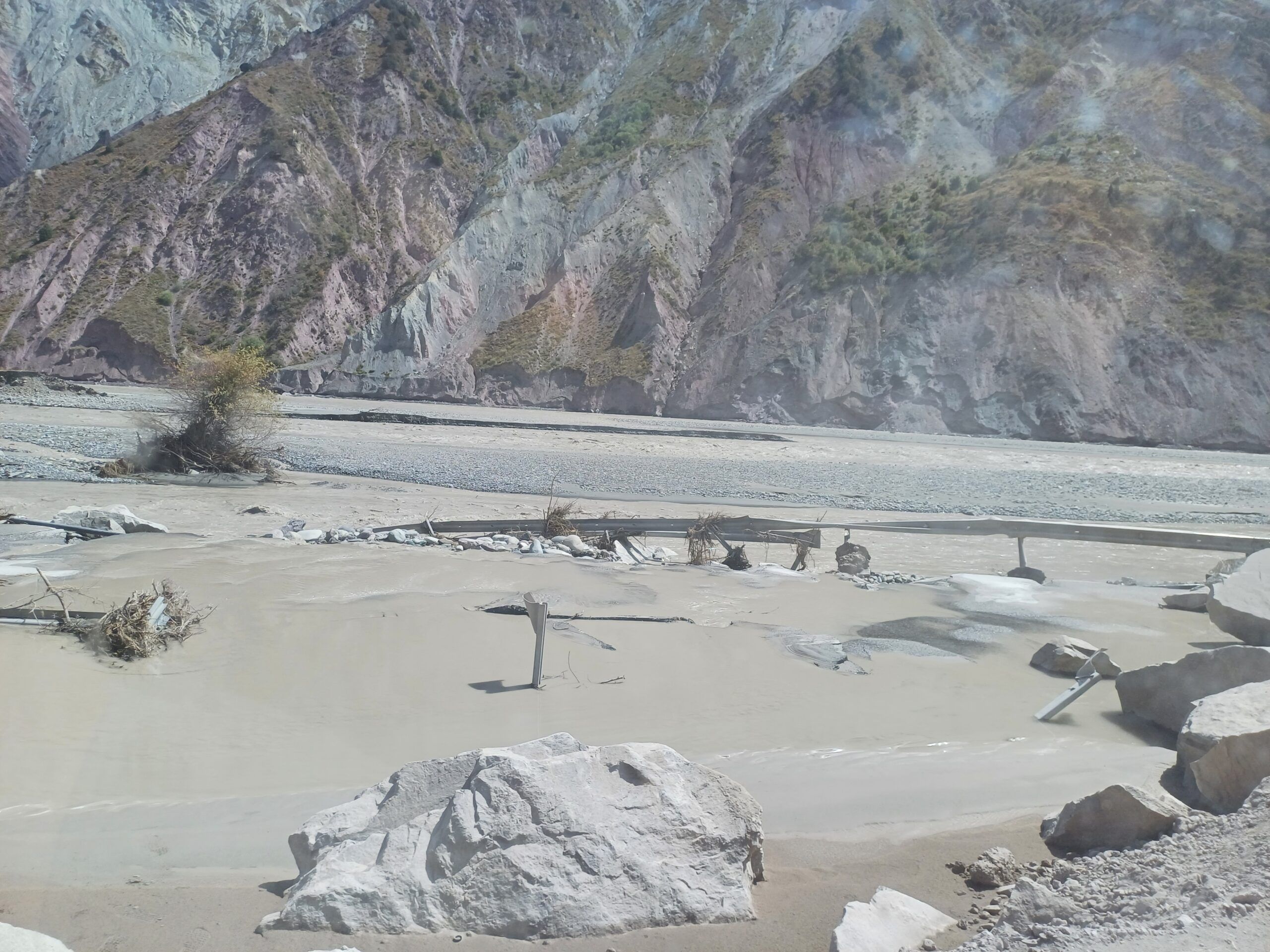
Наиболее опасным типом селей являются водно-ледниковые селевые потоки, которые обычно возникают после выхода из берегов ледниковых озер. Именно такое явление наблюдается на леднике Сайдой-Насафи (Баралмос), где в нижней части расположено несколько ледниковых озер. Эти озера образуются в нестабильных условиях и представляют серьезную угрозу для расположенных ниже по течению районов, включая международную дорогу, проходящую вдоль реки Сурхоб, и близлежащие населенные пункты.
-
История
По научным оценкам, с 1990 по 2019 год глобальный объем, площадь и количество ледниковых озер увеличились на 53%, а в Центральной Азии - примерно на 20%. Эта тенденция сохраняется в условиях продолжающегося потепления климата. В Таджикистане в период с 1997 по 2018 год было зарегистрировано более 4 100 стихийных бедствий, при этом наиболее частым и смертоносным видом опасности остаются сели. Их частота значительно возрастает в периоды сильных дождей.
На леднике Сайдой-Насафи (Баралмос) с 2018 года значительно участились случаи прорыва озер. В период с 2018 по 2021 год было зафиксировано пять прорывов. Только в 2023 году было официально зарегистрировано еще пять событий. Каждое из этих наводнений нанесло ущерб транспортной инфраструктуре вдоль реки Сурхоб, включая участки международной автомагистрали. В зону наибольшего риска попали дороги Душанбе-Лахш и Нурабад-Сангвор, а также села Жаилган, Майдонтерак, Дувана, Кушагба и мост Джилонди.
Кроме того, выходы ледниковых озер из ледника Баралмос привели к двум сходам селей в июле 2021 года, повредив шоссе Вахдат-Лахш. Ущерб от одного из этих событий оценивается в 20 миллионов сомони. Причинами стали быстрое таяние ледников, вызванное повышением температуры воздуха, и критическое переполнение озер.
-
Меры
Для снижения риска наводнений в результате прорыва ледниковых озер и их последствий в районе ледника Сайдой-Насафи (Баралмос) необходимо вести постоянный мониторинг ледниковых озер, совершенствовать возможности прогнозирования с помощью современных технологий, а также расширять системы раннего оповещения и связи в отдаленных горных районах. Также крайне важна информированность населения и обучение навыкам подготовки к чрезвычайным ситуациям, а также защита критически важных объектов инфраструктуры, таких как дороги и мосты. Дополнительные инженерные меры, такие как контролируемый дренаж озер и защитные сооружения, играют важную роль в снижении уязвимости к климатическим катастрофам.
-
Культурное значение
Ниже по течению реки Сурхоб расположены Рогунская и Нурекская гидроэлектростанции. Увеличение частоты и объема наводнений, связанных с выходом ледниковых озер из берегов, а также сопутствующие селевые потоки повышают риск возникновения крупных притоков в эти водохранилища. Такие события могут оказать значительное влияние на экономику страны, а также на экосистемы и окружающую среду.
-
Проект GLOFCA:
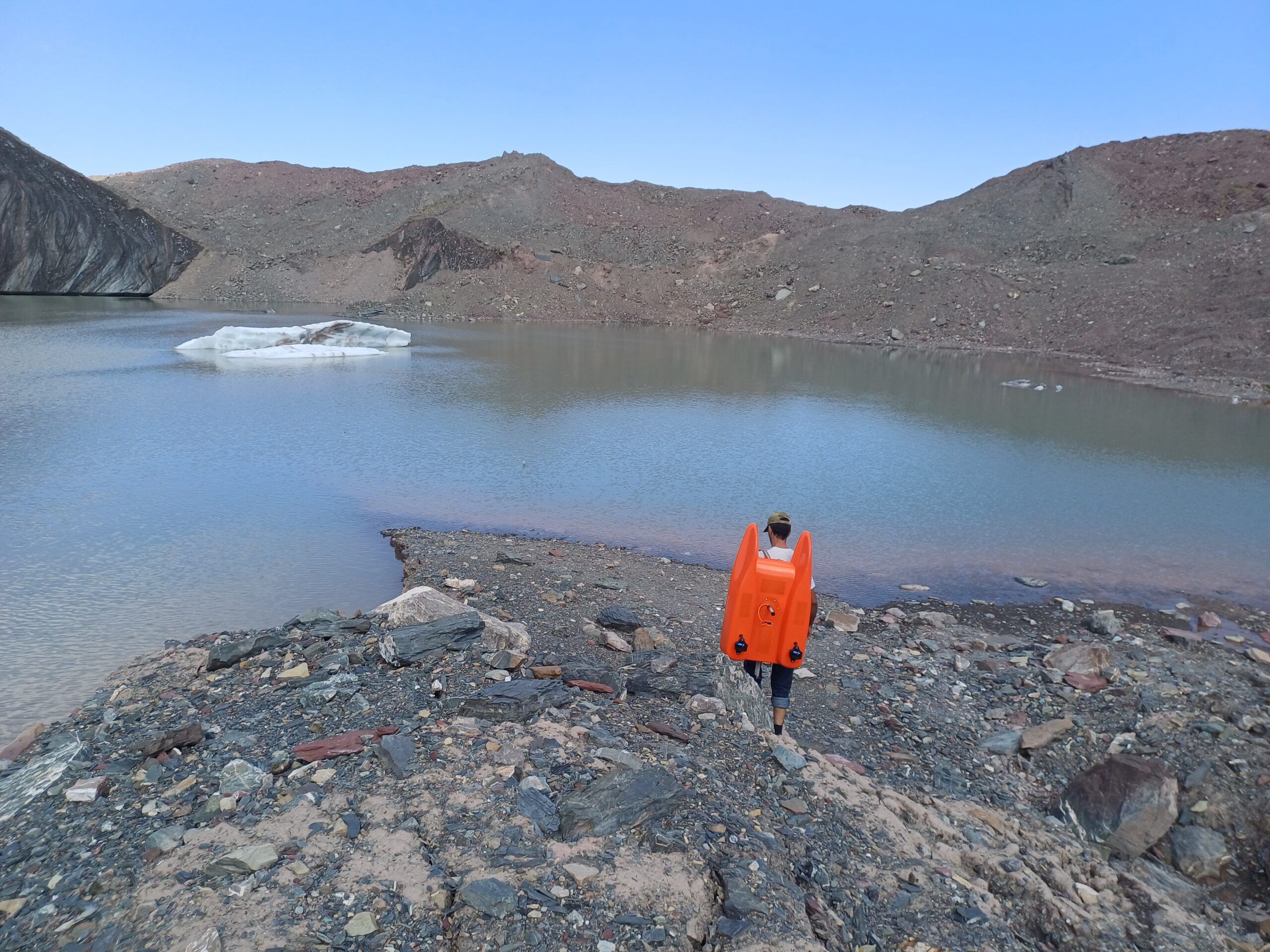
В рамках проекта GLOFCA в районе ледника Саидой-Насафи (Баралмос) реализуется ряд мер по снижению риска. Устанавливаются автоматические датчики для мониторинга накопления снега, температуры воздуха и осадков, а также системы радиосвязи и раннего оповещения для местных властей и общин. Проводятся регулярные батиметрические исследования для отслеживания эволюции и степени риска ледниковых озер. Также проводится моделирование опасностей и оценка зон повышенного риска.
В рамках проекта модернизируются системы сбора, обработки и интерпретации данных, включая динамические базы данных, платформы ГИС и компьютерное моделирование прорывов ледниковых озер и формирования селевых потоков. В наиболее уязвимых районах ведутся работы по укреплению склонов, включая строительство террасирующих сооружений. Также проводятся информационные кампании и обучающие программы, подкрепленные наглядными и аудиовизуальными материалами. Одним из ключевых мероприятий проекта является контролируемое осушение наиболее нестабильных ледниковых озер для предотвращения будущих извержений.